SEO

Advice for Dealing with a Negative SEO Attack
2018 is a different playing field for SEO than it was in 2017. Black hat techniques have become a dark art in modern SEO practices. The practice of using black hat strategies and other unethical tactics to damage a competitor’s rankings in search engines is known as a negative SEO attack. If your website is ranking well for highly-competitive keywords, you may be a target for such attacks.
Though negative SEO has existed for years, the strikes implemented today have grown more refined and sophisticated. Some negative SEO attacks can be virtually untraceable, and undetectable when they hit. What’s troubling about this is that you can’t always defend against a strike. Once a negative SEO attack hits you, recovering is messy and painstaking.
Search engines are continuously updating their algorithms to combat fake SEO advances being attained by users using black hat tactics. However, the best defense against a negative SEO attack is for you to be aware when erroneous shifts start to affect your website. The more you know about the different types of negative SEO attacks, the better you can protect yourself.
Four Types of Negative SEO Attacks – and How to Spot Them
While there are a number of ways a site’s SEO can be compromised, some common attacks on sites’ rankings include:
1. Pointing Spammy Links to Your Site
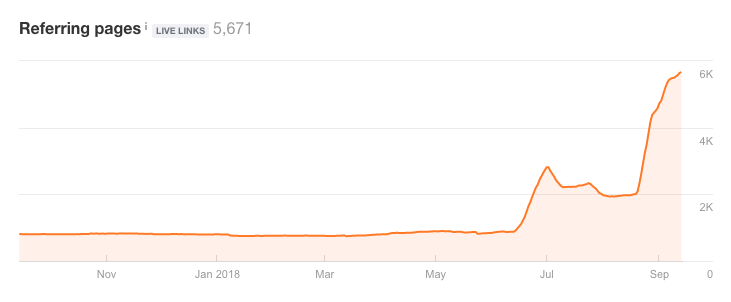
The best defense against a potential link attack is to constantly monitor your link profile growth. If you haven’t been working on building links and there is a sudden spike in link growth, that should raise a red flag. If your business exists on the web, a few spammy or unattractive links directed at your site is going to come with the territory. Search engines will not punish your site for this, even if it is reasonably new.
However, a continued barrage of spammy links pointing to internal pages could mean your site is under attack – and that a competitor is trying to push your website down in search engine result pages (SERPs).
Another similar, but more sophisticated tactic is adding canonical tags and flooding them with bad links. A black hat SEO will copy portions of your site onto spammy domains, then use canonical tags to point those spammy domains back to yours. The goal is for search engines like Google to devalue your site.
Google is aware of both of these tactics, which means they are actively fighting against link spam tactics like these through continual algorithm updates and manual actions. Nevertheless, if you suspect you are the victim of an off-page SEO attack like the ones listed here, you do have a course of action to take that will help combat the strike.
Solution – Perform regular link audits using a backlink tool like Ahrefs. If you see a huge spike or drop, see what unnatural links could be pointing to your site. Remove what bad links you can to protect your site’s brand and image, then upload a file containing the links you want to disavow using Google’s Disavow links page.
2. Copying Your Content and Pasting it Onto Other Sites
Creating good content is hard work, and not every law firm has the ability to create the content they need in order to rank well. Though the intentions of those who lift content from your site may not always be malignant, the negative SEO impact is. When someone takes information from your website and pastes it directly onto another online page, this action is known as scraping.
In a traditional negative SEO attack, the attacker will try to claim your content as their own in an attempt to bolster their own website and page ranking. What they claim their content to be could get indexed before yours, which would devalue your page. If you suspect you are the victim of an on-page SEO attack like this, you do have options.
Solution – Use a plagiarism detection service like Copyscape to detect if anyone has plagiarized your content. If they have, it is best to address the root of the problem and ask the site owner to remove your content. The site owner may refuse or not respond, and if that happens, do not worry. Fill out Google’s Copyright Removal form and report them.
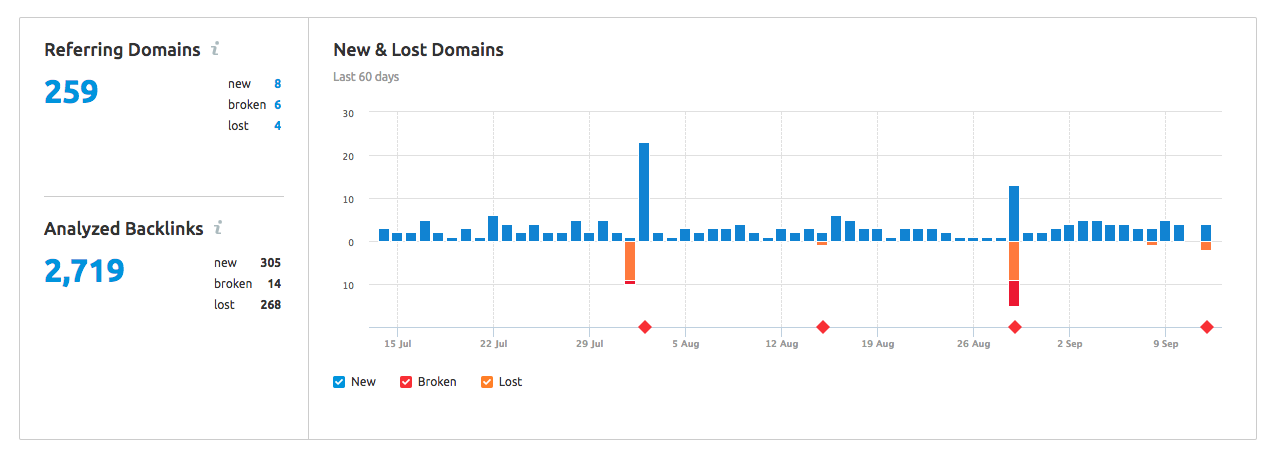
3. Removing High-Quality Links from Your Site
The importance of monitoring the health of your backlink profile cannot be stressed enough. Since Google Penguin launched in April 2012, site owners have been trying to clean up their backlink profile and increase the quality of links pointing back to their webpages. Sites that have acted to remove bad or spammy links can benefit from regained rankings, but this unfortunately paves opportunity for black hat SEO.
Fake link removal requests can have a devastating impact. In a sophisticated negative SEO attack, a competitor may register a domain name that is very similar to your own. The attacker can then redirect that new domain to your real domain. People who enter the fake domain will be redirected to yours, creating a false belief that the fake domain used to be an official one.
From there, the attacker can reach out to any high-quality website in your backlink profile asking them to remove the link. If you suspect you are the victim of an SEO attack like this one, there are steps you can take.
Solution – Run a backlink audit on SEMrush and review your referring domains. Make sure your backlinks are intact. SEMrush and other similar backlink audit tools like Ahrefs and Moz can indicate when a domain was added or lost. Unfortunately, the only way to repair this damage is to rebuild that link and explain to the webmaster or editor what happened, so it hopefully doesn’t happen again.
4. Hacking Your Site with On-Site Negative SEO
A negative SEO attacker could hack into your website and maliciously alter things. Hacking into a website is not easy, so on-site negative SEO attacks are less common. However, when they do happen, the effects can wipe your website from the SERPs.
If an attacker hacks into your site, spammy links can easily be dropped into it – and hidden. Another effective tactic would be to modify your content, successfully redirecting your webpages to theirs. A visitor would then land on your hacked page and automatically be redirected to the attacker’s page.
Another deceptive tactic would be to de-index your entire site. Be wary of previous site webmasters who may still have access to your domain. There are horror stories about SEO agencies who successfully de-indexed their ex-clients’ sites with a one-character alteration to their robots.txt file. For example, a Disallow: /wp-admin/ is acceptable, but a Disallow: / rule would de-index your entire site and prevent all web crawlers from accessing your site’s content. The best protection from an SEO attack like this one is to prevent it from ever happening.
Solution – Upgrade your website security and perform regular site audits. You can start by adopting a protocol used to provide additional security for your website to operate known as HTTPS. SSL/TLS implementation ensures that no one can intercept or change the content a user is viewing. The user is interacting directly with the server they are meant to be. As an added bonus, Google uses HTTPS as a ranking signal. Another tip: require that all users have complex passwords that are not on any vulnerable password list.
Final Words
The good news is Google is already well aware of these black hat techniques. Measures are continuously being taken to curtail a negative SEO attack before it impacts your site in SERPs, but black hat strategies and other unethical techniques are finding new ways to outsmart the system.
Always monitor your site’s performance. If you suspect you’ve been a target, do what you can to contain a negative SEO attack before the problem escalates. A large company with strong brand recognition and a high domain authority may not be affected by a negative SEO attack the same way a small business or law firm can be. Protecting your website properly may be too time-consuming, especially when you’re a new, upcoming business. An experienced legal marketing agency can help make your life easier. Give us a call at (614) 556-4618, or reach out online to learn how we can help.

Not sure where to begin?
Get started with a marketing audit.